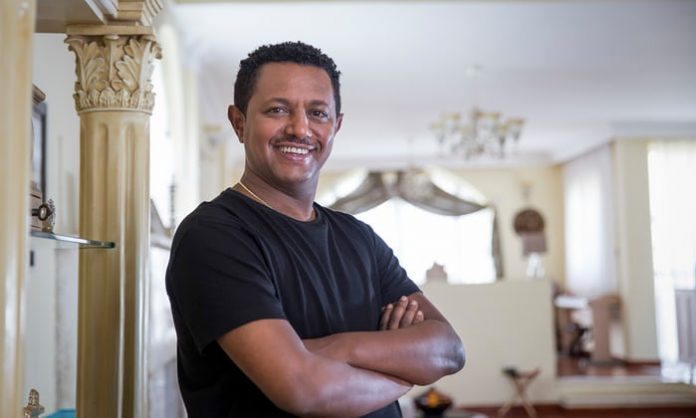
Tewodros Kassahun’s manager meets me on a quiet suburban road inside a gated compound. With their neoclassical mansions, manicured lawns and white picket fences, compounds such as this are a rarity in Ethiopia’s capital, Addis Ababa, and this one is as grand as it gets. Still, I’m underwhelmed as we turn in to the driveway of the house, which, by contrast with its neighbours, is relatively modest. This is, after all, the home of the biggest star in Ethiopian musical history: Teddy Afro.
He greets me in the living room, padding around in a tracksuit and socks. The house is in a bit of a mess, and he apologises – they’re clearing up the remains of an album launch party over the weekend. He and his manager are in high spirits. Three days earlier, they released Ethiopia, his fifth studio album; it had a record $650,000 recording budget, was the fastest-selling record in the country’s history, and topped Billboard’s world albums chart. Teddy’s relief is palpable – the release was beset by delays – as he settles into a chair and begins outlining his philosophy. “Art is closer to magic than logic,” he says, beaming cheerfully.
It is difficult to overstate Teddy Afro’s popularity and importance in Ethiopia today. “His level of celebrity is simply unprecedented,” says Heruy Arefe-Aine, the organiser of the country’s Ethiopian Music festival.
Ethiopia has long had a remarkably unified pop music culture – a national canon heard on buses and in bars across the country – but even in this context, Teddy stands out. He is the only artist of his generation to have risen to the level of Mahmoud Ahmed and Aster Aweke, the two greats of post-1960 Ethiopian pop, but at home at least he has comfortably outrun them both. Moreover, his significance reaches well beyond national borders: his popularity among the 2-million-strong Ethiopian diaspora, especially in the US, is unparalleled. The Ethio-Canadian R&B singer the Weeknd has cited him as a major influence.
But he is also a controversial figure. In 2008, he was imprisoned for a hit-and-run offence, which he has always denied he was responsible for. Many regard the jail sentence as a politically motivated move by Ethiopia’s authoritarian government, and a reaction to his 2005 album Yasteseryal, released in the year of a hotly disputed election. The lead single, whose video featured archive footage of the former emperor Haile Selassie and the bloody revolution that followed his reign, was interpreted by many as an indictment of everything that followed the emperor’s demise, including the current regime.
He became, perhaps somewhat unintentionally, a flag-waver for the Ethiopian opposition, a reputation he has maintained. The song is still, for all practical purposes, banned.
He makes for an unlikely political radical, and indeed his manager makes clear from the outset that politics is off the agenda. But he is nonetheless keen to explain the new album’s message. Lyrics are everything in Ethiopian music, and his – rich in idiom, allusion and wordplay – have excited his fans ever since he broke on to the scene in the early 00s. He argues that the country, under a state of emergency after violent anti-government protests last year, is slipping backwards. “We used to be a model for Africa,” he says, “but, because of our government, our country is divided.” The album is a call for unity and the rehabilitation of Ethiopia’s glorious past. “This younger generation is in a dilemma about their history,” he continues. “I feel a responsibility to teach them about the good things from their history. They should be proud of their achievements.”
Glancing references to the government aside, this is fairly inoffensive stuff. But in fact the politics are tricky. At the centre of the album is the story of Emperor Tewodros II, a 19th-century warrior-king whose rule is often seen as marking the beginning of modern Ethiopian history. “He fought and died for this country,” says Teddy, gesturing at a painting of the monarch on the living room wall, and pointing out that they share the same name. But the problem for many of Teddy’s critics is that his is a fiercely disputed view of that history. To many modern Ethiopians, Tewodros represents feudalism and imperialism. To some, his rule was characterised by the conquest and subjugation of other ethnic groups. But to his supporters, he united the country and resisted European colonialism.
Teddy’s previous album, Tikur Sew, released in 2012, did something similar for an even more controversial figure, Emperor Menelik II, hero of the Battle of Adwa in 1896, which saw the defeat of the invading Italians, but also the man responsible for the conquest of much of modern-day Ethiopia. Teddy, like Tewodros, Menelik and Selassie, hails from the Amharic-speaking part of Ethiopia; his critics see him as peddling a sort of nostalgic Amhara nationalism. His living room also contains an original sword belonging to Menelik, the old imperial flag, and a photograph of Selassie. “The younger generation need to know what our fathers did for this country,” he says. “It is clear that Menelik fought for Ethiopia, for unity, and against colonialism.”
Although the album Ethiopia contains an eclectic mix of influences (the second track, Semberé, could be by Manu Chao), and lyrics in several of Ethiopia’s 88 languages, Teddy remains in many ways an Amhara musician. He recalls sitting as a young child on the knee of Hirut Bekele, a popular Amhara vocalist from the 60s and 70s, as she performed in small clubs in Addis Ababa. “She was like a queen,” he remembers. His early work was reggae-infused but in his recent albums he has returned to a more recognisably Ethiopian sound, though funkier and insistently catchy. Traditional vibrato vocals, the itchy triplets of traditional Amharan rhythms, highly polished synth-heavy production: all this is the language of modern Ethiopian pop.
The latter has often been a source of frustration to Ethiopia’s musical old guard, who lament the lack of instrumentation among the younger generation, although Teddy points out that a live band plays on the album’s final track. He is a child of two musicians – his mother was a dancer who toured the world, his father a songwriter for a police orchestra in 50s Addis Ababa – but he came of age in the 80s under the military regime known as the Derg, when live music all but disappeared as a result of a strict overnight curfew that lasted for 16 years. Like most pop stars of his generation who began their career amid the heady post-Derg optimism of the late-90s club circuit, Teddy sings and plays keyboard.
It is perhaps for this reason that Teddy is almost unheard of beyond Ethiopia and its diaspora. Despite its distinctly Ethiopian vernacular, his music is still pop: cosmopolitan and perfect for dancing to. Musicians such as Mahmoud Ahmed or Mulatu Astatke (the father of Ethiopian jazz) appeal to western audiences drawn to a more exotic sound, complete with live bands. Teddy doesn’t offer that. But in any case, his focus is closer to home. “This is a dangerous time,” he says. “My priority now is Ethiopia.”
- This article was amended on 14 July, to reflect that Teddy Afro doesn’t hail from Amhara, but rather an Amharic-speaking region of Ethiopia.
Source: The Guardian